BSAG_Fahrplan_Sebaldsbrück_alt BSAG MOBILDIALOG
Die Linie RB25 (gummersbach Dieringhausen Bf) fährt von Marienheide Bf nach Gummersbach Dieringhausen Bf und hat 3 Stationen. RB25 Bahn Zeitplanübersicht für die kommende Woche: Eine Abfahrt am Tag um
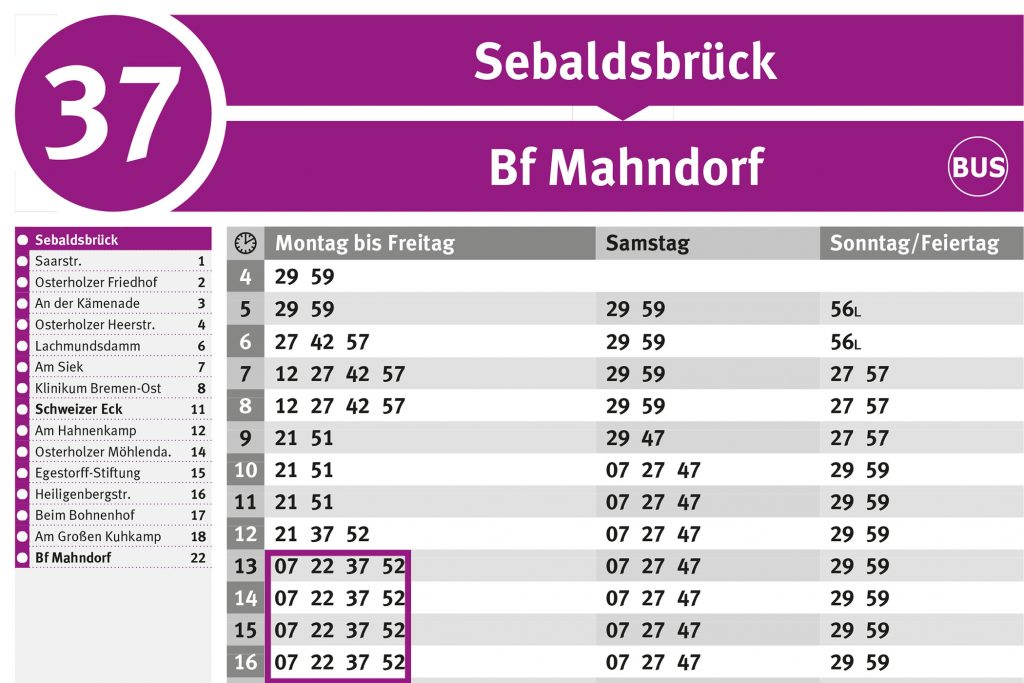
Die Linie RB25 (gummersbach Dieringhausen Bf) fährt von Marienheide Bf nach Gummersbach Dieringhausen Bf und hat 3 Stationen. RB25 Bahn Zeitplanübersicht für die kommende Woche: Eine Abfahrt am Tag um

Der kostengünstigste Flug von München nach Addis Ababa ist für nur 701 € im Mai 2024 erhältlich. *Bitte beachten Sie: Um Ihnen die größtmögliche Auswahl an Flugzielen anbieten zu können

إليك من يومياتي 7 عبارات تدل على قوة الشخصية وهي التي تؤكد لنا أن النّاس الذين يمتلكون ثقة عالية بالنّفس يحبون التحدي. يُنظر إلى الأشخاص الواثقين من أنفسهم على أنهم

Großes Mausohr. Das Große Mausohr oder auch nur Mausohr ( Myotis myotis) ist eine Fledermaus -Art aus der Gattung der Mausohren die 1797 von Borkhausen unter der Bezeichnung Vespertilio myotis

Top 10 Best Vinyl Stores in New York NY - April 2024 - Yelp - Rotten Island Records Westsider Records Village Revival Records Stranded Records NYC Legacy A1 Records Manhattan45

Legacy / Collide Boost 30 km/h. 13900 €. incl. 19% VAT plus shipping costs. Mit dem Boost Modul für Deinen Legacy oder Collide lässt sich die E Scooter von
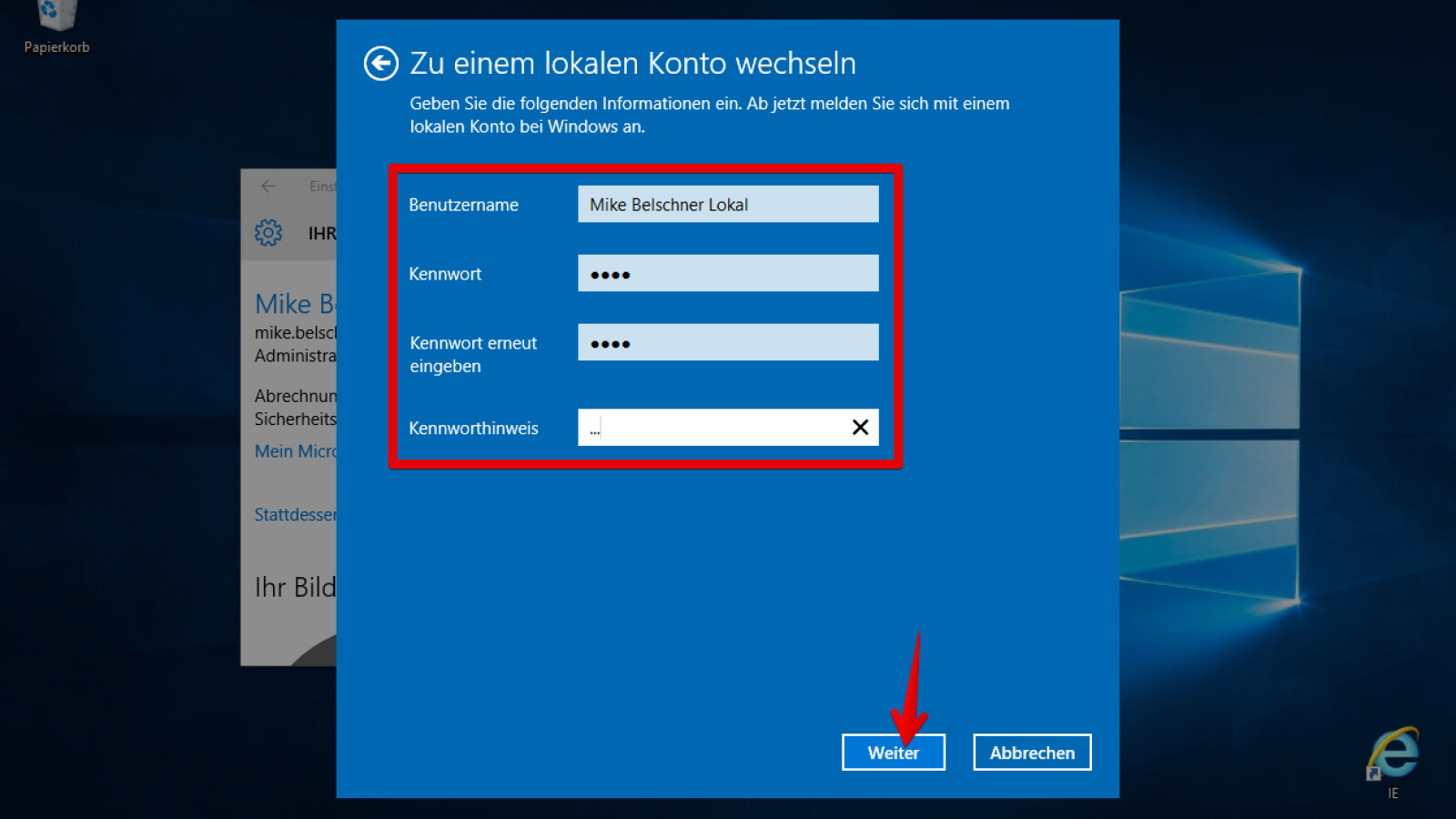
Liebe Kundinnen und Kunden! Haben Sie Fragen an die Quelle? Wir stehen Ihnen gerne mit Rat und Tat zur Seite. Hier haben wir die Antworten auf die derzeit häufigsten Fragen

Katy Perry - Hot N Cold (Lyrics)Get Hot N Cold from Katy Perry's 'One of the Boys'': http://katy.to/OneOfTheBoysKaty Perry Complete Collection on.

Staffel 1 und 2. Staffel 3. Staffel 4. Termine. Babylon Berlin Staffel 1 bis 4: sind jetzt im Abo über das Entertainment Plus Paket verfügbar und jederzeit über Sky Q